ECK is Elastic cloud on kubernetes - Kubernetes Operator pattern that extends basic kubernetes orchestration to easily deploy, secure, upgrade Elasticsearch and the rest of the stack such as kibana, logstash, various beats, and much more.
In my previous article I wrote about my kube.sh script which is a wrapper that installs a minikube environment to run your kubernetes projects. We will use the wrapper to deploy our kubernetes environment and start deploying elasticsearch using ECK. The steps below are not limited to my minikube wrapper script but you can follow the same process for any kubernetes environment.
Lets get our minikube environment up!
$ curl -fsSL https://raw.githubusercontent.com/jlim0930/scripts/master/kube.sh -o kube.sh
$ chmod +x kube.sh
$ ./kube.sh start
[DEBUG] minikube found.
[DEBUG] kubectl found.
[DEBUG] build minikube
[DEBUG] CPU will be set to 4 cores
❗ These changes will take effect upon a minikube delete and then a minikube start
[DEBUG] MEM will be set to 16005mb
❗ These changes will take effect upon a minikube delete and then a minikube start
😄 minikube v1.19.0 on Centos 7.9.2009
✨ Using the docker driver based on existing profile
👍 Starting control plane node minikube in cluster minikube
🏃 Updating the running docker "minikube" container ...
🐳 Preparing Kubernetes v1.20.2 on Docker 20.10.5 ...
🔎 Verifying Kubernetes components...
▪ Using image metallb/speaker:v0.8.2
▪ Using image metallb/controller:v0.8.2
▪ Using image gcr.io/k8s-minikube/storage-provisioner:v5
🌟 Enabled addons: storage-provisioner, metallb, default-storageclass
🏄 Done! kubectl is now configured to use "minikube" cluster and "default" namespace by default
▪ Using image metallb/speaker:v0.8.2
▪ Using image metallb/controller:v0.8.2
🌟 The 'metallb' addon is enabled
[DEBUG] minikube IP is: 192.168.49.2
[DEBUG] LoadBalancer Pool: 192.168.49.150 - 192.168.49.175Please note that we have a LoadBalancer Pool of 192.168.49.150-192.168.49.175. The range might be different on your machine but you should be able to browse or access these IP's from the same server/workstation.
ECK!
- We will install the operator(version 1.3.2)
- Create a 1 node ES 7.9.0 cluster
- Find the PASSWORD for the elastic user
- Create kibana 7.9.0 to for the ES cluster
- Expand the cluster to 3 nodes
- Update elasticsearch license
- Upgrade elasticsearch to 7.10.2
- Upgrade kibana to 7.10.2
- Upgrade the operator to 1.5.0
- SSL configuration
install 1.3.2 ECK Operator
Download and apply the operator: (most examples have you apply from the url but I like to download the yaml)
$ wget https://download.elastic.co/downloads/eck/1.3.2/all-in-one.yaml
--2021-04-18 20:39:11-- https://download.elastic.co/downloads/eck/1.3.2/all-in-one.yaml
Resolving download.elastic.co (download.elastic.co)... 34.120.127.130, 2600:1901:0:1d7::
Connecting to download.elastic.co (download.elastic.co)|34.120.127.130|:443... connected.
HTTP request sent, awaiting response... 200 OK
Length: 167494 (164K) [binary/octet-stream]
Saving to: 'all-in-one.yaml'
100%[===============================================================================================================================================================================================>] 167,494 --.-K/s in 0.03s
2021-04-18 20:39:11 (4.83 MB/s) - 'all-in-one.yaml' saved [167494/167494]
$ mv all-in-one.yaml all-in-one-1.3.2.yaml
$ kubectl apply -f all-in-one-1.3.2.yaml
namespace/elastic-system created
serviceaccount/elastic-operator created
secret/elastic-webhook-server-cert created
configmap/elastic-operator created
Warning: apiextensions.k8s.io/v1beta1 CustomResourceDefinition is deprecated in v1.16+, unavailable in v1.22+; use apiextensions.k8s.io/v1 CustomResourceDefinition
customresourcedefinition.apiextensions.k8s.io/apmservers.apm.k8s.elastic.co created
customresourcedefinition.apiextensions.k8s.io/beats.beat.k8s.elastic.co created
customresourcedefinition.apiextensions.k8s.io/elasticsearches.elasticsearch.k8s.elastic.co created
customresourcedefinition.apiextensions.k8s.io/enterprisesearches.enterprisesearch.k8s.elastic.co created
customresourcedefinition.apiextensions.k8s.io/kibanas.kibana.k8s.elastic.co created
clusterrole.rbac.authorization.k8s.io/elastic-operator created
clusterrole.rbac.authorization.k8s.io/elastic-operator-view created
clusterrole.rbac.authorization.k8s.io/elastic-operator-edit created
clusterrolebinding.rbac.authorization.k8s.io/elastic-operator created
service/elastic-webhook-server created
statefulset.apps/elastic-operator created
Warning: admissionregistration.k8s.io/v1beta1 ValidatingWebhookConfiguration is deprecated in v1.16+, unavailable in v1.22+; use admissionregistration.k8s.io/v1 ValidatingWebhookConfiguration
validatingwebhookconfiguration.admissionregistration.k8s.io/elastic-webhook.k8s.elastic.co createdYou can view the operator logs via the command below. Once the operator is up the logs will stop scrolling.
kubectl -n elastic-system logs -f statefulset.apps/elastic-operatorLets make sure that our operator is running
$ kubectl get svc --all-namespaces
NAMESPACE NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
default kubernetes ClusterIP 10.96.0.1 <none> 443/TCP 5m33s
elastic-system elastic-webhook-server ClusterIP 10.102.126.238 <none> 443/TCP 56s
kube-system kube-dns ClusterIP 10.96.0.10 <none> 53/UDP,53/TCP,9153/TCP 5m32s
$ kubectl get pods -n elastic-system
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
elastic-operator-0 1/1 Running 0 4m11s
$ kubectl get events -n elastic-system
LAST SEEN TYPE REASON OBJECT MESSAGE
32s Normal Scheduled pod/elastic-operator-0 Successfully assigned elastic-system/elastic-operator-0 to minikube
31s Normal Pulling pod/elastic-operator-0 Pulling image "docker.elastic.co/eck/eck-operator:1.3.2"
24s Normal Pulled pod/elastic-operator-0 Successfully pulled image "docker.elastic.co/eck/eck-operator:1.3.2" in 7.698773037s
23s Normal Created pod/elastic-operator-0 Created container manager
23s Normal Started pod/elastic-operator-0 Started container manager
21s Normal LeaderElection configmap/elastic-operator-leader elastic-operator-0_0d16d823-0c58-4a33-a241-f784980224a5 became leader
32s Normal SuccessfulCreate statefulset/elastic-operator create Pod elastic-operator-0 in StatefulSet elastic-operator successfulPlease ensure that your elastic-operator-0 is running and 1/1 is READY before moving ahead.
create 1 node ES 7.9.0
Before we continue lets verify the name of our StorageClass. minikube creates a StorageClass by default that we can use for our PV and PVC.
$ kubectl get sc
NAME PROVISIONER RECLAIMPOLICY VOLUMEBINDINGMODE ALLOWVOLUMEEXPANSION AGE
standard (default) k8s.io/minikube-hostpath Delete Immediate false 8m19sLets create our yaml. I grabbed a config from https://github.com/elastic/cloud-on-k8s/tree/master/config and edited it.
$ cat es1.yaml
apiVersion: elasticsearch.k8s.elastic.co/v1
kind: Elasticsearch
metadata:
name: es1
spec:
version: 7.9.0
nodeSets:
- name: default
config:
# most Elasticsearch configuration parameters are possible to set, e.g: node.attr.attr_name: attr_value
node.roles: ["master", "data", "ingest", "ml"]
# this allows ES to run on nodes even if their vm.max_map_count has not been increased, at a performance cost
# node.store.allow_mmap: false
podTemplate:
metadata:
labels:
# additional labels for pods
foo: bar
spec:
# this changes the kernel setting on the node to allow ES to use mmap
# if you uncomment this init container you will likely also want to remove the
# "node.store.allow_mmap: false" setting above
initContainers:
- name: sysctl
securityContext:
privileged: true
command: ['sh', '-c', 'sysctl -w vm.max_map_count=262144']
###
# uncomment the line below if you are using a service mesh such as linkerd2 that uses service account tokens for pod identification.
# automountServiceAccountToken: true
containers:
- name: elasticsearch
# specify resource limits and requests
resources:
limits:
memory: 1Gi
cpu: 1
env:
- name: ES_JAVA_OPTS
value: "-Xms512m -Xmx512m"
count: 1
# request 2Gi of persistent data storage for pods in this topology element
volumeClaimTemplates:
- metadata:
name: elasticsearch-data
spec:
accessModes:
- ReadWriteOnce
resources:
requests:
storage: 1Gi
storageClassName: standard
# inject secure settings into Elasticsearch nodes from k8s secrets references
# secureSettings:
# - secretName: ref-to-secret
# - secretName: another-ref-to-secret
# # expose only a subset of the secret keys (optional)
# entries:
# - key: value1
# path: newkey # project a key to a specific path (optional)
http:
service:
spec:
# expose this cluster Service with a LoadBalancer
type: LoadBalancer
# tls:
# selfSignedCertificate:
# # add a list of SANs into the self-signed HTTP certificate
# subjectAltNames:
# - ip: 192.168.1.2
# - ip: 192.168.1.3
# - dns: elasticsearch-sample.example.com
# certificate:
# # provide your own certificate
# secretName: my-certPlease take a note of the following
Deployment name: es1
Version: 7.9.0
Resource limits: 1CPU, 1GiB memory
JVM HEAP: 512M
Count: 1
storageClassName: standard
Storage: 1Gi
http: LoadBalancer
$ kubectl apply -f es1.yaml
elasticsearch.elasticsearch.k8s.elastic.co/es1 createdLet this run for a bit for the container image to be downloaded and cluster to start. If you have watch installed you can run watch -n 2 "kubectl get svc,pod to keep watch of changes to Services and Pods
$ kubectl get svc,pod
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
service/es1-es-default ClusterIP None <none> 9200/TCP 119s
service/es1-es-http LoadBalancer 10.100.238.185 192.168.49.150 9200:30635/TCP 2m
service/es1-es-transport ClusterIP None <none> 9300/TCP 2m
service/kubernetes ClusterIP 10.96.0.1 <none> 443/TCP 18m
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
pod/es1-es-default-0 1/1 Running 0 113s
$ kubectl get elasticsearch
NAME HEALTH NODES VERSION PHASE AGE
es1 green 1 7.9.0 Ready 4m11s
$ kubectl get pv,pvc
NAME CAPACITY ACCESS MODES RECLAIM POLICY STATUS CLAIM STORAGECLASS REASON AGE
persistentvolume/pvc-e67231d1-4eff-4a74-a4b5-a408efb2eb7a 1Gi RWO Delete Bound default/elasticsearch-data-es1-es-default-0 standard 11m
NAME STATUS VOLUME CAPACITY ACCESS MODES STORAGECLASS AGE
persistentvolumeclaim/elasticsearch-data-es1-es-default-0 Bound pvc-e67231d1-4eff-4a74-a4b5-a408efb2eb7a 1Gi RWO standard 11mTo view your cluster logs you can kubectl logs -f es1-es-default-0
find Password
Now that our instance is up lets find out what our password for elastic user is set to.
$ kubectl get pod
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
es1-es-default-0 1/1 Running 0 29m
$ PASSWORD=$(kubectl get secret es1-es-elastic-user -o go-template='{{.data.elastic | base64decode}}')
$ echo ${PASSWORD}
9NHn5L8k7KM0GB10E42hSI2a
$ curl -k -u "elastic:${PASSWORD}" https://192.168.49.150:9200
{
"name" : "es1-es-default-0",
"cluster_name" : "es1",
"cluster_uuid" : "OrQe8VcsSLSMWtm4TS_oaA",
"version" : {
"number" : "7.9.0",
"build_flavor" : "default",
"build_type" : "docker",
"build_hash" : "a479a2a7fce0389512d6a9361301708b92dff667",
"build_date" : "2020-08-11T21:36:48.204330Z",
"build_snapshot" : false,
"lucene_version" : "8.6.0",
"minimum_wire_compatibility_version" : "6.8.0",
"minimum_index_compatibility_version" : "6.0.0-beta1"
},
"tagline" : "You Know, for Search"
}
$ curl -k -u "elastic:${PASSWORD}" https://192.168.49.150:9200/_cluster/health?pretty
{
"cluster_name" : "es1",
"status" : "green",
"timed_out" : false,
"number_of_nodes" : 1,
"number_of_data_nodes" : 1,
"active_primary_shards" : 0,
"active_shards" : 0,
"relocating_shards" : 0,
"initializing_shards" : 0,
"unassigned_shards" : 0,
"delayed_unassigned_shards" : 0,
"number_of_pending_tasks" : 0,
"number_of_in_flight_fetch" : 0,
"task_max_waiting_in_queue_millis" : 0,
"active_shards_percent_as_number" : 100.0
}create kibana 7.9.0
As seen above elasticsearch cluster is up and running so lets configure kibana! Again it does take a while to get the image downloaded and started so keep checking the status. Don't forget about watch -n 2 "kubectl get svc,pod
$ cat kibana-es1.yaml
apiVersion: kibana.k8s.elastic.co/v1
kind: Kibana
metadata:
name: kibana-es1
spec:
version: 7.10.2
count: 1
elasticsearchRef:
name: "es1"
#http:
# service:
# spec:
# type: LoadBalancer
# this shows how to customize the Kibana pod
# with labels and resource limits
podTemplate:
metadata:
labels:
foo: bar
spec:
containers:
- name: kibana
resources:
limits:
memory: 1Gi
cpu: 1
http:
service:
spec:
type: LoadBalancer
$ kubectl apply -f kibana-es1.yaml
kibana.kibana.k8s.elastic.co/kibana-es1 created
$ kubectl get svc,pod
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
service/es1-es-default ClusterIP None <none> 9200/TCP 5m17s
service/es1-es-http LoadBalancer 10.109.248.35 192.168.49.150 9200:31446/TCP 5m19s
service/es1-es-transport ClusterIP None <none> 9300/TCP 5m19s
service/kibana-es1-kb-http LoadBalancer 10.98.18.204 192.168.49.151 5601:31679/TCP 2m40s
service/kubernetes ClusterIP 10.96.0.1 <none> 443/TCP 8m55s
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
pod/es1-es-default-0 1/1 Running 0 5m17s
pod/kibana-es1-kb-86bc58f47-frx7c 1/1 Running 0 2m37s
$ kubectl get kibana
NAME HEALTH NODES VERSION AGE
kibana-es1 green 1 7.9.0 2m43sAnd now we are able to login
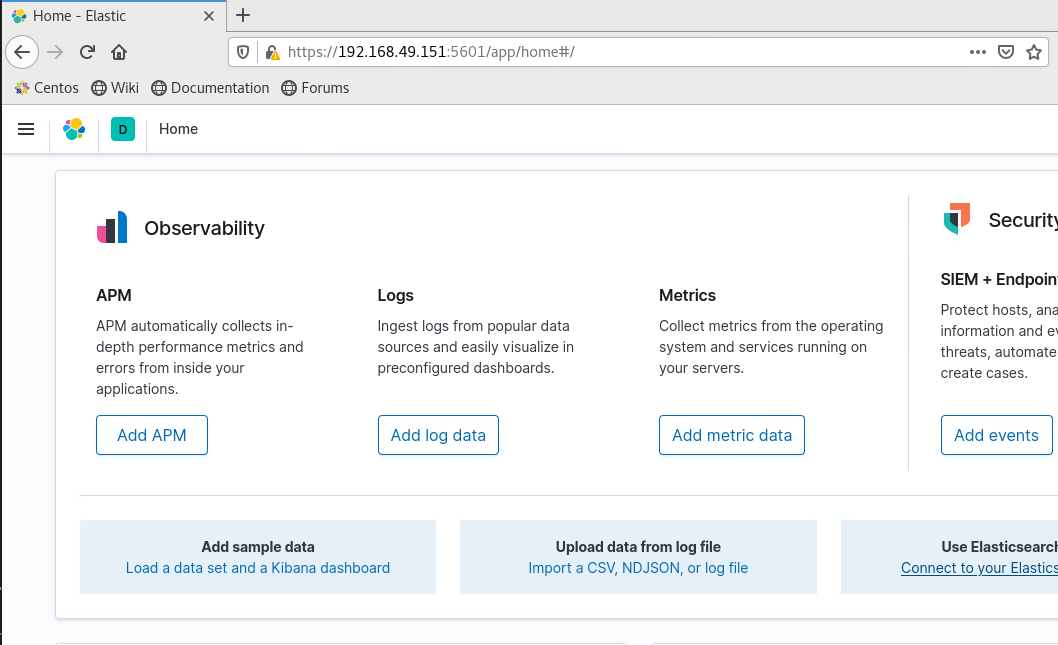
expand to 3 nodes
Lets edit our es1.yaml and change the count to 3 and reapply the yaml
$ cat es1.yaml | grep "count:"
count: 1
$ sed -i 's/count: 1/count: 3/g' es1.yaml
$ cat es1.yaml | grep "count:"
count: 3
$ kubectl apply -f es1.yaml
elasticsearch.elasticsearch.k8s.elastic.co/es1 configured
$ kubectl get pod,svc
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
pod/es1-es-default-0 1/1 Running 0 13m
pod/es1-es-default-1 1/1 Running 0 2m18s
pod/es1-es-default-2 1/1 Running 0 87s
pod/kibana-es1-kb-86bc58f47-frx7c 1/1 Running 0 10m
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
service/es1-es-default ClusterIP None <none> 9200/TCP 13m
service/es1-es-http LoadBalancer 10.109.248.35 192.168.49.150 9200:31446/TCP 13m
service/es1-es-transport ClusterIP None <none> 9300/TCP 13m
service/kibana-es1-kb-http LoadBalancer 10.98.18.204 192.168.49.151 5601:31679/TCP 10m
service/kubernetes ClusterIP 10.96.0.1 <none> 443/TCP 16m
$ curl -k -u "elastic:${PASSWORD}" https://192.168.49.150:9200/_cat/nodes?v
ip heap.percent ram.percent cpu load_1m load_5m load_15m node.role master name
172.17.0.8 21 76 57 0.37 0.64 0.60 dilm - es1-es-default-2
172.17.0.6 58 76 48 0.37 0.64 0.60 dilm - es1-es-default-1
172.17.0.5 42 83 24 0.37 0.64 0.60 dilm * es1-es-default-0Now we have a 3 node cluster! One thing to note is that since Pod and Services are separated even though you are making changes to the Pods the Service remains the same and visa versa.
upload a license
Lets take a look at the default license
$ curl -k -u "elastic:${PASSWORD}" https://192.168.49.150:9200/_license
{
"license" : {
"status" : "active",
"uid" : "a36d560e-5d61-4784-a12e-b1183dd2f88f",
"type" : "basic",
"issue_date" : "2021-04-19T21:11:00.872Z",
"issue_date_in_millis" : 1618866660872,
"max_nodes" : 1000,
"issued_to" : "es1",
"issuer" : "elasticsearch",
"start_date_in_millis" : -1
}
}
# Get usage data
$ kubectl -n elastic-system get configmap elastic-licensing -o json | jq .data
{
"eck_license_level": "basic",
"enterprise_resource_units": "1",
"timestamp": "2021-04-19T22:41:04Z",
"total_managed_memory": "4.29GB"
}Lets try to update the license. I have a license file named license.json
$ kubectl create secret generic eck-license --from-file=license.json -n elastic-system
secret/eck-license created
$ kubectl label secret eck-license "license.k8s.elastic.co/scope"=operator -n elastic-system
secret/eck-license labeled
$ curl -k -u "elastic:${PASSWORD}" https://192.168.49.150:9200/_license
{
"license" : {
"status" : "active",
"uid" : "xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx",
"type" : "platinum",
"issue_date" : "xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx",
"issue_date_in_millis" : xxxxxxxxxxx,
"expiry_date" : "xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx",
"expiry_date_in_millis" : xxxxxxxxxxx,
"max_nodes" : 250,
"issued_to" : "xxxxxxxxxxxx",
"issuer" : "API",
"start_date_in_millis" : xxxxxxxxxx
}
}
# Get usage data
$ kubectl -n elastic-system get configmap elastic-licensing -o json | jq .data
{
"eck_license_level": "enterprise",
"enterprise_resource_units": "1",
"max_enterprise_resource_units": "250",
"timestamp": "2021-04-19T22:43:04Z",
"total_managed_memory": "4.29GB"
}upgrade to es 7.10.2
Now lets upgrade from 7.9.0 to 7.10.2
$ curl -k -u "elastic:${PASSWORD}" https://192.168.49.150:9200
{
"name" : "es1-es-default-2",
"cluster_name" : "es1",
"cluster_uuid" : "OrQe8VcsSLSMWtm4TS_oaA",
"version" : {
"number" : "7.9.0",
"build_flavor" : "default",
"build_type" : "docker",
"build_hash" : "a479a2a7fce0389512d6a9361301708b92dff667",
"build_date" : "2020-08-11T21:36:48.204330Z",
"build_snapshot" : false,
"lucene_version" : "8.6.0",
"minimum_wire_compatibility_version" : "6.8.0",
"minimum_index_compatibility_version" : "6.0.0-beta1"
},
"tagline" : "You Know, for Search"
}
$ cat es1.yaml | grep 7.9.0
version: 7.9.0
$ sed -i 's/7.9.0/7.10.2/g' es1.yaml
$ cat es1.yaml | grep 7.10.2
version: 7.10.2
$ kubectl apply -f es1.yaml
elasticsearch.elasticsearch.k8s.elastic.co/es1 configuredgo grab some coffee since this will take a while.... The order of operation is listed on https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/cloud-on-k8s/1.5/k8s-orchestration.html#k8s-upgrade-patterns
$ kubectl get svc,pod
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
service/es1-es-default ClusterIP None <none> 9200/TCP 111m
service/es1-es-http LoadBalancer 10.109.248.35 192.168.49.150 9200:31446/TCP 111m
service/es1-es-transport ClusterIP None <none> 9300/TCP 111m
service/kibana-es1-kb-http LoadBalancer 10.98.18.204 192.168.49.151 5601:31679/TCP 108m
service/kubernetes ClusterIP 10.96.0.1 <none> 443/TCP 114m
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
pod/es1-es-default-0 1/1 Running 0 2m35s
pod/es1-es-default-1 1/1 Running 0 4m35s
pod/es1-es-default-2 1/1 Running 0 7m35s
pod/kibana-es1-kb-86bc58f47-frx7c 1/1 Running 0 108m
$ curl -k -u "elastic:${PASSWORD}" https://192.168.49.150:9200
{
"name" : "es1-es-default-0",
"cluster_name" : "es1",
"cluster_uuid" : "OrQe8VcsSLSMWtm4TS_oaA",
"version" : {
"number" : "7.10.2",
"build_flavor" : "default",
"build_type" : "docker",
"build_hash" : "747e1cc71def077253878a59143c1f785afa92b9",
"build_date" : "2021-01-13T00:42:12.435326Z",
"build_snapshot" : false,
"lucene_version" : "8.7.0",
"minimum_wire_compatibility_version" : "6.8.0",
"minimum_index_compatibility_version" : "6.0.0-beta1"
},
"tagline" : "You Know, for Search"
}upgrade to kibana 7.10.2
Now we can follow similar method to upgrade kibana to 7.10.2
$ cat kibana-es1.yaml | grep 7.9.0
version: 7.9.0
$ sed -i 's/7.9.0/7.10.2/g' kibana-es1.yaml
$ cat kibana-es1.yaml | grep 7.10.2
version: 7.10.2
$ kubectl apply -f kibana-es1.yaml
kibana.kibana.k8s.elastic.co/kibana-es1 configured
$ kubectl get svc,pod
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
service/es1-es-default ClusterIP None <none> 9200/TCP 115m
service/es1-es-http LoadBalancer 10.109.248.35 192.168.49.150 9200:31446/TCP 115m
service/es1-es-transport ClusterIP None <none> 9300/TCP 115m
service/kibana-es1-kb-http LoadBalancer 10.98.18.204 192.168.49.151 5601:31679/TCP 112m
service/kubernetes ClusterIP 10.96.0.1 <none> 443/TCP 119m
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
pod/es1-es-default-0 1/1 Running 0 6m44s
pod/es1-es-default-1 1/1 Running 0 8m44s
pod/es1-es-default-2 1/1 Running 0 11m
pod/kibana-es1-kb-66cf497d55-whkjz 1/1 Running 0 2m34s
Now to check:
upgrade operator to 1.5.0
Currently we are running 1.3.2 operator
$ kubectl -n elastic-system describe pod elastic-operator-0 |grep "Image:"
Image: docker.elastic.co/eck/eck-operator:1.3.2Lets follow directions on https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/cloud-on-k8s/1.5/k8s-deploy-eck.html to upgrade our operator
$ ANNOTATION='eck.k8s.elastic.co/managed=false'
$ kubectl annotate --overwrite elasticsearch es1 $ANNOTATION
elasticsearch.elasticsearch.k8s.elastic.co/es1 annotated
$ kubectl annotate --overwrite elastic --all $ANNOTATION
elasticsearch.elasticsearch.k8s.elastic.co/es1 annotated
kibana.kibana.k8s.elastic.co/kibana-es1 annotated
$ for NS in $(kubectl get ns -o=custom-columns='NAME:.metadata.name' --no-headers); do kubectl annotate --overwrite elastic --all $ANNOTATION -n $NS; done
elasticsearch.elasticsearch.k8s.elastic.co/es1 annotated
kibana.kibana.k8s.elastic.co/kibana-es1 annotated
$ kubectl apply -f all-in-one-1.5.0.yaml
namespace/elastic-system configured
serviceaccount/elastic-operator configured
secret/elastic-webhook-server-cert configured
configmap/elastic-operator configured
Warning: apiextensions.k8s.io/v1beta1 CustomResourceDefinition is deprecated in v1.16+, unavailable in v1.22+; use apiextensions.k8s.io/v1 CustomResourceDefinition
customresourcedefinition.apiextensions.k8s.io/agents.agent.k8s.elastic.co created
customresourcedefinition.apiextensions.k8s.io/apmservers.apm.k8s.elastic.co configured
customresourcedefinition.apiextensions.k8s.io/beats.beat.k8s.elastic.co configured
customresourcedefinition.apiextensions.k8s.io/elasticsearches.elasticsearch.k8s.elastic.co configured
customresourcedefinition.apiextensions.k8s.io/enterprisesearches.enterprisesearch.k8s.elastic.co configured
customresourcedefinition.apiextensions.k8s.io/kibanas.kibana.k8s.elastic.co configured
clusterrole.rbac.authorization.k8s.io/elastic-operator configured
clusterrole.rbac.authorization.k8s.io/elastic-operator-view configured
clusterrole.rbac.authorization.k8s.io/elastic-operator-edit configured
clusterrolebinding.rbac.authorization.k8s.io/elastic-operator configured
service/elastic-webhook-server configured
statefulset.apps/elastic-operator configured
Warning: admissionregistration.k8s.io/v1beta1 ValidatingWebhookConfiguration is deprecated in v1.16+, unavailable in v1.22+; use admissionregistration.k8s.io/v1 ValidatingWebhookConfiguration
validatingwebhookconfiguration.admissionregistration.k8s.io/elastic-webhook.k8s.elastic.co configured
$ kubectl -n elastic-system get pod
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
elastic-operator-0 1/1 Running 0 49s
$ RM_ANNOTATION='eck.k8s.elastic.co/managed-'
$ kubectl annotate elasticsearch es1 $RM_ANNOTATION
elasticsearch.elasticsearch.k8s.elastic.co/es1 annotated
$ kubectl -n elastic-system describe pod elastic-operator-0 | grep "Image:"
Image: docker.elastic.co/eck/eck-operator:1.5.0SSL configuration
By default transport and http will be encrypted via self signed certs however if you want to control it a bit more you can set the subjectAltNames for your certificates or provide your own certificates.
Self-signed Certificate:
To generate self signed certificates edit the following in es1.yaml and kibana-es1.yaml
es1.yaml
http:
service:
spec:
# expose this cluster Service with a LoadBalancer
type: LoadBalancer
loadBalancerIP: 192.168.49.150
tls:
selfSignedCertificate:
# add a list of SANs into the self-signed HTTP certificate
subjectAltNames:
- ip: 192.168.49.150
- ip: 127.0.0.1
# - dns: elasticsearch-sample.example.com
# certificate:
# # provide your own certificate
# secretName: my-certkibana-es1.yaml
http:
service:
spec:
type: LoadBalancer
loadBalancerIP: 192.168.49.151
tls:
selfSignedCertificate:
subjectAltNames:
- ip: 192.168.49.151
- ip: 127.0.0.1You can extract the CA certificate:
$ kubectl get secret | grep es-http
es1-es-http-ca-internal Opaque 2 179m
es1-es-http-certs-internal Opaque 3 179m
es1-es-http-certs-public Opaque 2 179m
$ kubectl get secret es1-es-http-ca-internal -o go-template='{{index .data "tls.crt" | base64decode }}' > ca.crt
$ curl --cacert ./ca.crt -u "elastic:${PASSWORD}" https://192.168.49.150:9200
{
"name" : "es1-es-default-1",
"cluster_name" : "es1",
"cluster_uuid" : "OrQe8VcsSLSMWtm4TS_oaA",
"version" : {
"number" : "7.10.2",
"build_flavor" : "default",
"build_type" : "docker",
"build_hash" : "747e1cc71def077253878a59143c1f785afa92b9",
"build_date" : "2021-01-13T00:42:12.435326Z",
"build_snapshot" : false,
"lucene_version" : "8.7.0",
"minimum_wire_compatibility_version" : "6.8.0",
"minimum_index_compatibility_version" : "6.0.0-beta1"
},
"tagline" : "You Know, for Search"
}Disable TLS
You can disable TLS for http by adding this
spec:
http:
tls:
selfSignedCertificate:
disabled: truemonitoring cluster/metricbeat/filebeat
To be continued....
Thanks for reading and if you have any suggestions on how to make this better or more use cases please let me know!
Use Case - How to install plugins
According to https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/cloud-on-k8s/1.4/k8s-snapshots.html#k8s-install-plugin to install plugins you can create your own container images or add it as init container.
Added this to my elastic yaml in the PodTemplate -> initContainers section
- name: install-plugin
command:
- sh
- -c
- |
bin/elasticsearch-plugin install --batch repository-azure repository-s3Once my pods were up I went to take a look and there it was
$ kubectl exec -it es1-es-default-0 /bin/bash
# bin/elasticsearch-plugin list
repository-azure
repository-s3Now to setup secrets
Encode your account and key
$ echo -n 'account-name' | base64
$ echo -n 'encrypted-account-name' | base64Create secrets.yaml with the following
apiVersion: v1
kind: Secret
metadata:
name: snapshot-secret
type: Opaque
data:
azure.client.default.account: <Output from previous steps>
azure.client.default.key: <Output from previous step>Apply the yaml kubectl apply -f secrets.yaml
Update the main es1.yaml with
spec:
secureSettings:
- secretName: snapshot-secretNow your ready to configure your repository
PUT _snapshot/azure_backup
{
"type": "azure",
"settings": {
"container": "my_container",
"base_path": "/"
}
}Verify your repo
POST /_snapshot/azure_backup/_verify
2 Comments